A variety of adhesive types readily bond copper and its alloys. Many prefer adhesives over soldering as adhesives do not heat damage the copper.
Anaerobic adhesives cure in the presence of metal and the absence of oxygen. Copper is one of the most reactive metals, so the anaerobic adhesive will set up and cure much more quickly than the time listed for fixture speed on steel.
Anaerobic applications include threadlocking, thread sealing, form-in-place gaskets, weld sealing, retaining, and munitions sealing.
For threadlocking, permanent and removable grades are available in various viscosities (from wicking grades to high viscosity grades. Specialty products for use with potable water are also available. Select a product based on the strength and gap (or bolt size) you require.
Thread sealants are also available for sealing threaded pipe connections. Specialty grades for hydraulics contain no fillers, which could cause blockages. Other specialty grades include; oxygen contact, potable water grades, and UL Classified grades.
For form-in-place gasketing consider Permabond LH197 is flexible and easier to remove from soft metals.
Retaining compound product selection is heavily based on gap fill requirements. Permanently bond brass co-axial non-threaded joints with retaining compounds.
Cyanoacrylate adhesives or instant adhesives are ideal for bonding copper. Methyl cyanoacrylates such as the original Permabond 910, create strong bonds. The bonds have high shear strength; however, the application may require a structural adhesive if you are bonding copper and require resistance to polar solvents or impact.
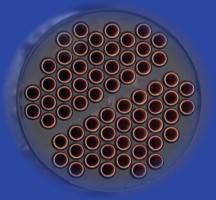
All grades bond well. Choose an adhesive based on the type of cure method you prefer for your application. Single component epoxies cure with heat. Two component epoxies cure when you mix the components. A common epoxy application is to pot tubing in heat exchangers.
There are several types of structural acrylics.
Surface-activated acrylics cure by applying a water-thin initiator to one surface and the resin to the other. They begin to cure as soon as you join the two components.
Bead on Bead acrylics – A bead of one part is dispensed onto a bead of the other. Sufficient mixing of the two components occurs when the components are joined, and the adhesive squeezed into a thin bond line.